Discover the Women of the Hall
These are the Inductees of the National Women’s Hall of Fame. Select any of the women to discover their stories and learn how they have influenced other women and this country.
 Louise McManus
Science
1896
1994
Louise McManus
Science
1896
1994

Louise McManus
First American nurse to earn a Ph.D. Louise McManus was central to the establishment of schools of nursing in colleges and universities, providing the fundamental basis for nursing science growth.
 Grace Hopper
Science
1906
New York
1994
Grace Hopper
Science
1906
New York
1994

Grace Hopper
A mathematics genius and computer pioneer, Grace Hopper created computer programming technology that forever changed the flow of information and paved the way for modern data processing. In 1952, Hopper was credited with creating the first compiler for modern computers, a program that translates instructions written by a programmer into codes that can be read by a computer. Hopper was the first woman to hold the rank of Rear Admiral in the U.S. Navy.
 Maria Mitchell
Science
1818
Massachusetts
1994
Maria Mitchell
Science
1818
Massachusetts
1994

Maria Mitchell
An astronomer who discovered a new comet in 1847, Maria Mitchell was the first woman named to membership in the American Academy of Arts & Sciences. She was also a founder of the Association for the Advancement of Women.
 Antonia Novello
Government, Science
1944
Puerto Rico
1994
Antonia Novello
Government, Science
1944
Puerto Rico
1994

Antonia Novello
First woman and first Hispanic to be named Surgeon General of the United States. A pediatrician, Novello has used her position to alleviate suffering worldwide, especially for women and children.
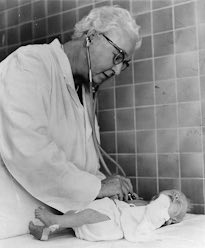 Virginia Apgar
Science
1909
New Jersey
1995
Virginia Apgar
Science
1909
New Jersey
1995

Virginia Apgar
Physician best known for development of the Apgar Score in 1952. This system of simple tests is used to determine whether a newborn child requires special medical attention, and it has saved thousands of lives.
 Ann Bancroft
Education, Science
1955
Minnesota
1995
Ann Bancroft
Education, Science
1955
Minnesota
1995

Ann Bancroft
First woman to travel across the ice to the North and South Poles. She was the first woman to travel across Greenland on skis, and in 1993, was leader of the American Women’s Expedition, a group of four who skied more than 600 miles to the South Pole.
 Mary Breckinridge
Science
1881
Tennessee
1995
Mary Breckinridge
Science
1881
Tennessee
1995

Mary Breckinridge
The United States foremost pioneer in the development of midwifery and provision of care to rural areas. Breckinridge founded the Frontier Nursing Service.
 Lillian Moller Gilbreth
Science
1878
California
1995
Lillian Moller Gilbreth
Science
1878
California
1995

Lillian Moller Gilbreth
Industrial engineer and expert in motion studies, Gilbreth was a pioneer in the relationship between engineering and human relations. She convinced managers that worker-efficiency is the result of the quality of the work environment.
 Eileen Collins
Science
1956
New York
1995
Eileen Collins
Science
1956
New York
1995

Eileen Collins
First American woman to pilot a spacecraft. A math teacher at the Air Force Academy and test pilot, Collins served as pilot of the space shuttle Discovery during a mission to rendezvous with space station Mir. In July, 1999 she became NASA’s first female commander in space.
 Anne Morrow Lindbergh
Arts, Science
1906
1996
Anne Morrow Lindbergh
Arts, Science
1906
1996

Anne Morrow Lindbergh
Author of numerous elegant essays, journals and other books. Lindbergh also excelled as co-pilot and navigator with her husband Charles on their historic flights to promote the development of international aviation.
 Maria Goeppert-Mayer
Science
1906
Germany
1996
Maria Goeppert-Mayer
Science
1906
Germany
1996

Maria Goeppert-Mayer
First U.S. woman and second woman ever to win the Nobel Prize in Physics. The Prize was awarded for developing the shell model of the nucleus of the atom, the basic model for the description of nuclear properties. Mayer was also a member of the team that first isolated fissionable uranium 235.
 Gerty Theresa Radnitz Cori
Science
1896
Czech Republic
1998
Gerty Theresa Radnitz Cori
Science
1896
Czech Republic
1998

Gerty Theresa Radnitz Cori
First American woman to receive the Nobel Prize in science. Cori, along with her husband and Bernardo Houssay of Argentina, received the award in 1947 “for their discovery of the course of the catalytic conversion of glycogen.” Their work, the first bioengineering of a large biological molecule in a test tube, became the foundation for our understanding of how cells use food and convert it to energy.
 Chien-Shiung Wu
Science
1912
China
1998
Chien-Shiung Wu
Science
1912
China
1998

Chien-Shiung Wu
Nuclear physicist whose pioneering work altered modern physical theory and changed the accepted view of the structure of the universe.
 Shannon W. Lucid
Science
1943
1998
Shannon W. Lucid
Science
1943
1998

Shannon W. Lucid
A commercial, instrumental and multi-engine-rated pilot, Dr. Shannon Lucid was a member of the first astronaut class to admit women (1979). In her more than 30 year tenure with NASA, she served in various capacities and participated in five space flights. Dr. Lucid was the first woman to hold an international record for the most flight hours in orbit by any non-Russian, and, until June 2007, she held the record for the most flight hours in orbit by any woman in the world – 5,354 hours or 223 days in space.
 Florence Wald
Science
1916
New York
1998
Florence Wald
Science
1916
New York
1998

Florence Wald
Former dean of the Yale School of Nursing and founder of the Hospice movement in America, for which she was awarded the honorary Doctorate of Medical Sciences by Yale University in 1995. As a nurse, she went to Europe to study Hospice from the ground up.
 Shirley Ann Jackson
Education, Science
1946
District of Columbia
1998
Shirley Ann Jackson
Education, Science
1946
District of Columbia
1998

Shirley Ann Jackson
First woman to chair the United States Nuclear Regulatory Commission and the first African American woman to serve on the Commission. Elected a Fellow of the American Physical Society for her contribution to physical science, she became an advocate for women in the areas of science, education and public policy. As Chair of NRC, she rearticulated the vision of the NRC to include reaffirmation of the basic health and safety mission of the agency.
 Marjory Stoneman Douglas
Science
1890
Minnesota
2000
Marjory Stoneman Douglas
Science
1890
Minnesota
2000

Marjory Stoneman Douglas
A journalist with the Miami News Record, she was an active leader in the Florida suffrage movement and an environmentalist credited with saving the Everglades as a national resource. Douglas authored over ten books and several plays, including The Everglades: River of Grass. After receiving the Presidential Medal of Freedom in 1993 at the age of 103, she remained an active and influential environmentalist to her death.
 Frances Oldham Kelsey
Science
1914
Canada
2000
Frances Oldham Kelsey
Science
1914
Canada
2000

Frances Oldham Kelsey
A medical and pharmaceutical researcher for the Food and Drug Administration, she refused to approve the use of thalidomide in this country, saving countless babies from terrible deformities. As a result of her testimony before Congress, the 1962 drug act was passed, giving the FDA greater control over the manufacture, testing and distribution of drugs. During a career with the FDA which spanned over 39 years, her supervision of clinical investigators has institutionalized the protection of the patient in drug investigations.
 Sylvia A. Earle
Science
1935
New Jersey
2000
Sylvia A. Earle
Science
1935
New Jersey
2000

Sylvia A. Earle
An undersea explorer since age 13, Earle became an internationally recognized marine biologist, author, lecturer and scientific consultant. Denied the opportunity to participate in the U.S. Navy “Tektite Project” to study the ocean, she founded “Tektite II”, an all-female expedition that spent two weeks exploring the ocean floor. The founder of two companies to design and build undersea vehicles, she is chief scientist and consultant to oceanographic and marine research centers throughout the world.
 Mary Edwards Walker
Philanthropy, Science
1832
New York
2000
Mary Edwards Walker
Philanthropy, Science
1832
New York
2000

Mary Edwards Walker
First female surgeon in the U.S. Army, she continually crossed the Confederate lines to treat civilians. After being taken prisoner in 1864 and imprisoned in Richmond, she was awarded the Congressional Medal of Honor, the first woman to receive this award. In 1917, her medal, along with 910 others, was taken away when Congress revised the standards to include only “actual combat with the enemy.” She refused to return the medal, wore it until her death, and it was finally awarded to her posthumously.
 Faye Glenn Abdellah
Science
1919
New York
2000
Faye Glenn Abdellah
Science
1919
New York
2000

Faye Glenn Abdellah
First nurse to hold the rank of Rear Admiral and the title of Deputy Surgeon General for the United States. She developed the first tested coronary care unit. A national pioneer in nursing research, she has authored or co-authored more than 150 publications and helped change the focus of nursing from disease-centered to patient-centered.
 Annie Dodge Wauneka
Science
1910
Arizona
2000
Annie Dodge Wauneka
Science
1910
Arizona
2000

Annie Dodge Wauneka
First woman elected to the Tribal Council, she became determined to lead the fight against tuberculosis among the Navajo. She wrote a dictionary to translate English words for modern medical techniques into Navajo, and hosted a radio broadcast in the Navajo language to explain how modern medicine could help in better care for pregnant women and new babies and other family health problems.
 Dorothy H. Andersen
Science
1901
North Carolina
2001
Dorothy H. Andersen
Science
1901
North Carolina
2001

Dorothy H. Andersen
Pediatrician and pathologist who was the first to identify cystic fibrosis and developed a simple, definitive diagnostic test for the disease.
 Bessie Coleman
Science
1892
Texas
2001
Bessie Coleman
Science
1892
Texas
2001

Bessie Coleman
The first licensed black female aviator. She earned her international pilot’s license in 1921 and gained fame during the next five years for her air acrobatics and highflying stunts. She dreamed of starting a school to train black aviators.
